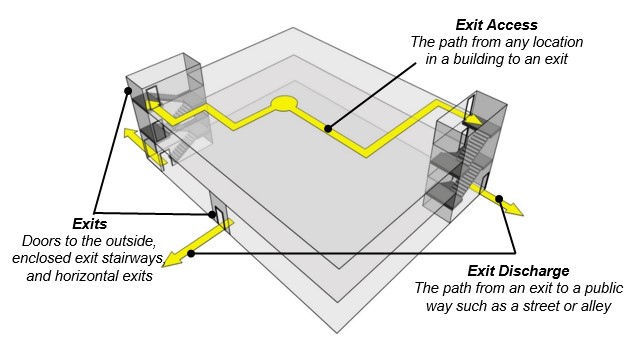
Have you ever heard of tow operators? they are the busiest personnel in the event of a traffic accident. So what’s interesting about this topic? in this topic serves as an introduction to operating at incidents involving fuel cell vehicles. Vehicle types, hydrogen properties, systems, and vehicle safety systems are all addressed.
This video also covers vehicle recovery and towing considerations specific to fuel cell vehicles, including safety procedures.
Main differences
The single most essential difference between fuel cells and batteries is simple: a battery stores energy which it then uses, whereas a fuel cell generates energy by converting available fuel. As long as you have access to the fuel, you have access to electricity – anytime, anywhere. Interestingly, a fuel cell can also have a battery component to store the energy it is generating.
Types of Fuel Cells
- POLYMER ELECTROLYTE MEMBRANE FUEL CELLS
- DIRECT METHANOL FUEL CELLS
- ALKALINE FUEL CELLS
- PHOSPHORIC ACID FUEL CELLS
- MOLTEN CARBONATE FUEL CELLS
- SOLID OXIDE FUEL CELLS
- REVERSIBLE FUEL CELLS
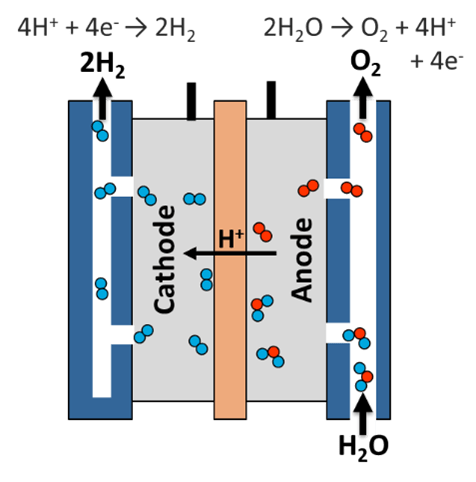
Hydrogen can be produced from the electrolysis process
How Does it Work?
Like fuel cells, electrolyzers consist of an anode and a cathode separated by an electrolyte. Different electrolyzers function in different ways, mainly due to the different type of electrolyte material involved and the ionic species it conducts.
Source : NFPA, ENERGY.GOV, UMICORE